e-Learning Ecologies MOOC’s Updates
What is Blended Learning?
Blended learning combines the best of two training environments—traditional face-to-face classroom training and high-tech eLearning. By covering all the bases, you can engage all types of learners—those who learn better in a structured environment that includes face-to-face interaction with an instructor, and independent types who learn better with semi-autonomous, computer-based training (1). While students still attend "brick-and-mortar" schools with a teacher present, face-to-face classroom practices are combined with computer-mediated activities regarding content and delivery (2).
Fig. 1. What is Blended Learning? (URL 1)
While the classroom offers an opportunity for role-playing with immediate face-to-face feedback, online learning offers personalized, self-paced learning with eLearning /mLearning components that lend themselves to interactive media such as skill-building, games, videos, tutorials, quizzes and social media components, all accessible from the learner’s home page in the Learning Management System (LMS)—and accessible from the learner’s smartphone or tablet (1).
Fig 2. Implement a Blended Learning Strategy (URL 2)
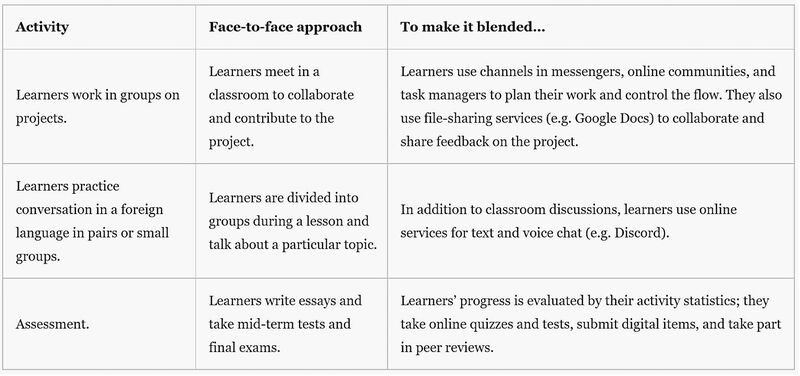
Here are some examples of how blended learning works (3):
There are a few models through which blended learning can be implemented in schools. They include the following approaches:
- Face-to-face driver – where the teacher drives the instruction and augments with digital tools.There are a few models through which blended learning can be implemented in schools. They include the following approaches:
- Rotation – students cycle through a schedule of independent online study and face-to-face classroom time.
- Flex – Most of the curriculum is delivered via a digital platform and teachers are available for face-to-face consultation and support.
- Labs – All of the curriculum is delivered via a digital platform but in a consistent physical location. Students usually take traditional classes in this model as well.
- Self-blend – Students choose to augment their traditional learning with online course work.
- Online driver – Students complete an entire course through an online platform with possible teacher check-ins. All curriculum and teaching is delivered via a digital platform and face-to-face meetings are scheduled or made available if necessary (2).
There are many components that can comprise a blended learning model, including "instructor-delivered content, e-learning, webinars, conference calls, live or online sessions with instructors, and other media and events, for example, Facebook, e-mail, chat rooms, blogs, podcasting, Twitter, YouTube, Skype and web boards (2).
Blended instruction is reportedly more effective than purely face-to-face or purely online classes. Blended learning methods can also result in high levels of student achievement more effective than face-to-face learning (2). The advantages of blended learning are (4):
- Hybrid learning is focused on reducing the overall costs of education by routing classroom discussions and texts on free open-source platforms of information. It is considered as a one-time investment as once the students have procured the electronic device, then learning can be facilitated without any recurring costs.
- Schedule: Blended learning is a more flexible approach to education as students get to sign in to class projects and various operations whenever they want and complete tasks at their convenience without adhering to the rigid time restrictions of a traditional classroom setting.
- Learner led learning: In this approach, the student gets primacy in deciding the course and approach to tackle curriculums and various other projects. It is a more learner driven approach wherein the student directly participates in the process of teaching and facilitation. As mentioned earlier, since blended learning is more flexible, it gives students the leeway to continue studies at their own pace without exerting undue pressure on them. Such self-paced learning gives more control to the student to make decisions about when they want to move ahead with a particular material.
- Increased participation: A hybrid of classroom and online teaching helps students to be more proactive learners as opposed to the mindless passive absorption of information in classrooms.
- Higher levels of personalization: Students get to learn and understand concepts at their own pace. Online participation also gives them ample opportunities to interact with industry professionals and teachers for review and feedback.
- Extended reach: Students get to explore avenues that are outside the purview of a classroom. Students can reach out to a wide range of professionals and online sources that can give them a deeper insight into the concepts taught in classrooms.
Disadvantages of using blended learning are (5);
- The Technology Can Be Challenging Rather Than Useful: One of the key issues is the technological literacy, which can be a real problem for teachers. Not all digital resources are reliable and easy to use.
- Blended Learning Makes Teachers Overwork: There is a great deal of additional work for teachers involved in all stages of blended learning. They have to broaden their horizons, pick the most suitable syllabus, and apply significantly more time and effort to find the right balance between online and face-to-face learning. Unfortunately, not all of them are willing to do so.
- Students Can Experience Cognitive Load, too: With a great range of possibilities provided by the blended learning model, teachers may start overdoing with educational activities and content.
- Credibility of Sources and Plagiarism Become Even Bigger Issue: Having a digital-friendly educational environment may cause more plagiarizing from online resources. Moreover, there are a number of unreliable online resources that present false or misinterpreted facts.
Additional Videos:
References:
- What is Blended Learning? A Guide to Everything You Need to Know https://elmlearning.com/blended-learning-everything-need-know/
- Blended learning https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blended_learning
- What is Blended Learning and How Can It Be Used? https://www.ispringsolutions.com/blog/blended-learning-a-primer
- Benefits of Blended learning https://medium.com/tegs/benefits-of-blended-learning-a1420d90d298
- Pros And Cons Of Blended Learning At College https://elearningindustry.com/pros-cons-blended-learning-at-college
URL 1: https://sd33.bc.ca/sites/sd33.bc.ca/files/2020-06/Hybrid%20Learning.png
URL 2: https://www.teachthought.com/learning/12-types-of-blended-learning/
Additional Links:
- 5 questions to ask now to shape blended learning of the future https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/05/5-questions-to-ask-now-to-shape-blended-learning-of-the-future/
- What Do We Mean by Blended Learning? https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11528-019-00375-5
- The Past, Present and Future of Blended Learning: An in Depth Analysis of Literature https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275543451_The_Past_Present_and_Future_of_Blended_Learning_An_in_Depth_Analysis_of_Literature
- A Study on Students’ Views on Blended Learning Environment https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/156422
- Towards an intelligent blended system of learning activities model for New Zealand institutions: an investigative approach https://www.nature.com/articles/s41599-020-00696-4
Videos:
- Blended learning: creating your unique blend https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w4ovBQ3uyh0&t=19s
- What is blended learning, and how does it work in practice? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fjXdvgHNSX4
- Blended learning is here to stay, but which aspects of digital teaching will universities keep? https://www.timeshighereducation.com/hub/blackboard/p/blended-learning-here-stay-which-aspects-digital-teaching-will-universities-keep
- Driving learning outcomes with blended learning https://www.timeshighereducation.com/hub/coursera/p/driving-learning-outcomes-blended-learning
- The Basics of Blended Learning https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3xMqJmMcME0
Infographics:
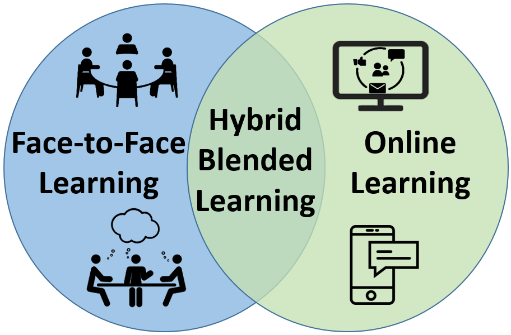



blended learning is when two different ways of learning is embedded in a system. First is face to face learning and second is through the use of internet and online.
Update #1: ON BLENDED LEARNING
It is undeniable that education was among the sectors changed so drastically by the COVID-19 pandemic. Schools nationwide were forced to close when physical classes were considered too risky to hold as SARS Cov2, the virus that causes COVID-19 is transmitted mainly from human to human and whether vaccines would be available remained uncertain.
Confronted with this, the Department of Education (DepEd) turned to what is now known as BLENDED LEARNING for the current school year to date. The DepEd solution required schools to shift from conventional to “hybrid” learning, so-called because it involved a mix of distant online learning and modules delivered to students’ doorsteps or picked up from DepEd sites. Electronic media delivered by the internet, radio, and TV broadcasts to mobile devices, computers, TV, and radio sets became a necessary component of blended, or hybrid, learning.
Aside from being used as a temporary solution for schools and classrooms shuttered by the pandemic, blended learning could also address the problems that have been perennially plaguing conventional learning. Among these are the lack of teachers and facilities and other problems that blended learning could address. Blended learning requires students to attend classes at home, which would prompt parents to be capable of helping their children with lessons.
The reality, however, would sink in for those who neither have the financial means, nor the time, for blended learning. The difficulties of access to information communication technology (ICT) are felt most by students. Children from impoverished areas were likely to be at a disadvantage at the start of classes.
Aside from the difficulty in access to internet services with enough speed for blended learning, increasing internet subscription costs also hound learners and instructors. Hardware and software, must-haves in blended learning, could be costly to everyone—educators, students, and parents.
As criticisms and problems pile up over its version of mixed learning, the DepEd tried to clarify that it was not claiming success. So, as DepEd struggles with blended learning woes, several local government units (LGUs) had stepped up to the plate to help learners and teachers.
Reference: https://newsinfo.inquirer.net/1362497/the-promises-and-pitfalls-of-blended-learning-in-ph