Jennie J. Jones’s Updates
1A Update: Does PBIS Promote Equity in K-12 Schools?
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is an evidence-based, tiered framework for supporting students’ behavioral, academic, social, emotional, and mental health.(“What is PBIS?’ 2020). This nationally popular program purports to support equity within schools if implemented with fidelity, however, some educators believe the opposite to be true. The PBIS model heavily focuses on Behaviorism, which is largely boiled down to controlling or managing a student’s outward behaviors to affect the appearance of being on-task. Whether a student actually is on-task or they actually care about the thing they are attempting often is of no real importance to the behaviorist. Alfie Kohn said,”...researchers continue to find that the more you reward people for doing something, the more they lose interest in whatever they had to do to get the reward. Often, too, they end up not doing it as well as those who weren’t treated like bundles of behaviors to be managed and manipulated”(Kohn, 2018). PBIS forces students into compliance through extrinsic rewards such as points, tickets, and prizes. Often, students tend to lose interest in those extrinsic rewards and do not continue desired behavior for a sustained time.
Moreover, the PBIS system is based on a neurotypical, culturally white set of expectations in schools. When thinking about what behaviors we expect in school, it is important to ask, “Who is determining the behaviors? On what prevailing basis do we decide what is acceptable?”
Dr. Knestict, author of Controlling Our Children; Hegemony and Deconstructing the Positive Behavioral Intervention Support Model posits,” You could be a field-sensitive learner, and that learner needs interaction. They need language. They need to talk about what they’re learning. And they need to share it with other people. Then there’s field-independent, and it’s all internal with them. Our schools are predominantly field-independent places. They don’t encourage that discussion and noise and collaboration and working with things. If we reward the field-independent learners, we automatically disadvantage the field-sensitive learners. And the other piece to that is that field-sensitive learners are predominantly underrepresented people.” When considering the multiple types of learners in our classrooms, PBIS requires that all students comply with a rigid set of behaviors that do not consider intrinsic motivations or engagement with a meaningful curriculum. Culturally and diversity sensitive educators understand the need for relationships and engagement over manipulative tactics in order to provide an environment for deep learning. Therefore, the PBIS system of behavior management is not conducive to equity in education, according to some experts. Since some states have mandated the PBIS system in many of our public schools, the question remains,” How can we better serve all students with sensitivity and respect for various cultures and backgrounds?”
Center on PBIS(2022). Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports [Website].www.pbis.org
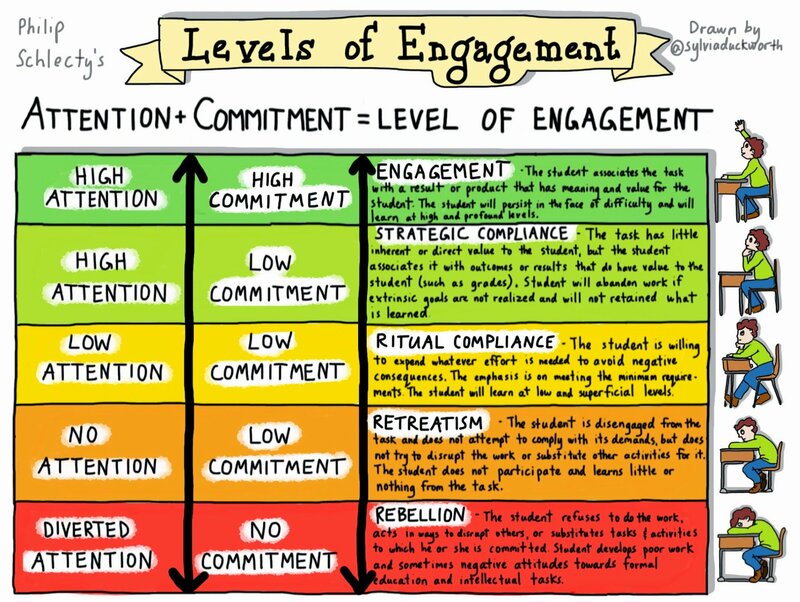
Duckworth, S. (2015). Philip Schlecty’s Levels of Engagement [Drawing].https://twitter.com/sylviaduckworth/status/594979332742864898
Kohn, A. (2022, March 14). Students aren't lab rats. stop treating them like they are (opinion). Education Week. Retrieved August 28, 2022, from https://www.edweek.org/teaching-learning/opinion-students-arent-lab-rats-stop-treating-them-like-they-are/2018/09
Phillips, J. (2020, November 12). #vted reads about PBIS. Innovative Education in VT. Retrieved August 28, 2022, from https://tiie.w3.uvm.edu/blog/vted-reads-pbis/#.YAmYGuhKhEY


I faced a similar conundrum when a one-size-fits-all approach, like PBIS, stifled my creativity as a field-sensitive learner. The Slice Master of classroom management seemed skewed to reward only those who fit the dominant mold, making it hard for diverse students to shine. This highlights why educational models must be more adaptable and culturally aware.
Having worked in schools using PBIS, I’ve seen how the focus on external rewards can sometimes miss the deeper needs of students, especially those from diverse backgrounds. I’ve found that incorporating engaging, interest-driven activities—like playing Sprunki Retake , a music game that encourages creativity and collaboration—can help foster intrinsic motivation and a more inclusive environment. It’s about finding ways to connect beyond behavior management to truly support every learner.
https://www.sp2dzy.com/
This is a really interesting point about PBIS! Never thought about how it might favor some kids over others. Makes you wonder if there's a better way to support everyone fairly.@Chill Guy Clicker
like
Interesting take on PBIS! I always wondered if it really helped everyone, or just made kids who already fit in feel even more comfortable. Makes you think about who we're really helping with these systems.crazy cattle 3d ai barbie doll list compare
level devil - not a troll game is a 2D platformer full of unexpected traps and obstacles. Get your character to the exit door, overcome hidden challenges, and level up.
Sometimes, you just want to play a game that’s pure fun, and that’s exactly what animal rampage 3d delivers. It doesn’t need a complex story or high-end graphics to be awesome. The gameplay is simple—just destroy everything—but that simplicity is its strength. You can pick it up, play for five minutes or thirty, and always walk away entertained. It’s ideal for casual gamers or anyone who wants a quick dose of chaos with cute animal skins.
you can explore their services further here
Experience the captivating visuals and sound design in escape road city 2. It’s a feast for the senses!